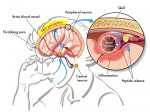
Theres nothing like the pounding intensity of a migraine. Everything gets louder, brighter, and sharper. The world distills to a single point of painful focus, usually on one side of the head. When you are in it, all you want is for the pain to stop, and its likely that youll be so nauseous that you vomit.
Any physical movement, bright light, or loud sound can make it worse, and usually the only thing to do is lie down in a dark room with a lavender eye pillow and hope you fall asleep.
A migraine is a pain in the head (different from a headache) that can last anywhere from 2 hours to 3 days. Many migraine sufferers can experience as many as three or four a week, though for most people it is much less frequent.
Migraines can be caused by genetic factors, emotional stress, fatigue, caffeine, eating food additives such as nitrates and MSG, alcohol, exposure to environmental toxins, changing weather patterns, skipping meals, illnesses like asthma and stroke, or abnormal sleep conditions. By far, emotional stress is the most common trigger.
Types of Migraines
~ Classic Migraines
These migraines are preceded by visual or sensory symptoms, called an aura. The aura can appear as flashing lights, spots, zig-zaging lines, or blind spots in one or both eyes. It can also affect other senses and produce sensations like ringing in the ears, difficulty speaking clearly, numbness or tingling in some part of the body, or smelling a strange odor.
Auras usually start about an hour before a migraine kicks in, and can last for anywhere from 15 minutes to an hour, or even during the entire migraine.
~ Common Migraines
Called so because they are the most common types, affecting about 80 percent of migraine sufferers, these migraine have no auras. They are usually signified or accompanied by fatigue, anxiety, extreme mood changes, and inability to focus.
~ Menstrual Migraines
Migraines that are caused by or connected to a womans fluctuating estrogen levels. Some can be helped by food or herbal hormone management.
~ Retinal or Ocular Migraine
Temporary total or partial loss of vision in one eye. May or may not include head pain.
~ Basilar Artery Migraine
Usually seen in young adults or those experiencing hormonal fluctuations. Head pain in the back of the head, usually with an aura of dizziness, mental confusion, challenges speaking, or sensory illusions.
~ Chronic Migraine (a.k.a. Tension-Type Headache, Transformed Migraine, or Co-existing Migraine)
When a migraine transforms into a constant background headache that seems to never fully go away, periodically flaring up into intense migraine symptoms.
~ Abdominal Migraine
Pain in the abdomen that can last up to 3 days, usually accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
~ Ophthalmoplegic Migraine
Pain that develops into partial or complete paralysis of the nerves used to move the eyes. This is one of the few types of migraine that requires immediate medical treatment.
~ Status Migrainosus
Extremely rare head pain that lasts longer than 3 days. Also requires medical treatment.
Doctors do not yet know how to cure most migraines. They will usually tell you to take aspirin, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen. Some people find relief with natural anti-inflammatories and soothing essential oils, but not all.
The best advice is to pay attention to what happens around you before you get a migraine, and avoid the foods, smells, and activities that seem to trigger it.
As stress, fatigue, and dehydration seems to make them worse, strive to get lots of rest, eat healthy food on a regular schedule, drink plenty of pure water, and practice stress-relieving techniques like Yoga and meditation.